Restarting the OpenSARLab Server and Notebook Kernel
Restarting the OpenSARLab Server
Overview
Restarting the server triggers the nbgitpuller.
Consider a case where:
- You have deleted or altered a notebook in the ASF notebook library and want to retrieve the original.
- There is a notebook update that you wish to pull in changes from the asf-jupyter-notebook repo.
A quick solution in either of those cases is to restart your server to run the nbgitpuller.
NB: If you are comfortable with git, you could do a git pull from
the terminal or in a notebook instead. However, do not push your changes as it may interfere with the nbgitpuller
Steps to Restart the Server
-
Select
Hub Control Panelfrom theFilemenu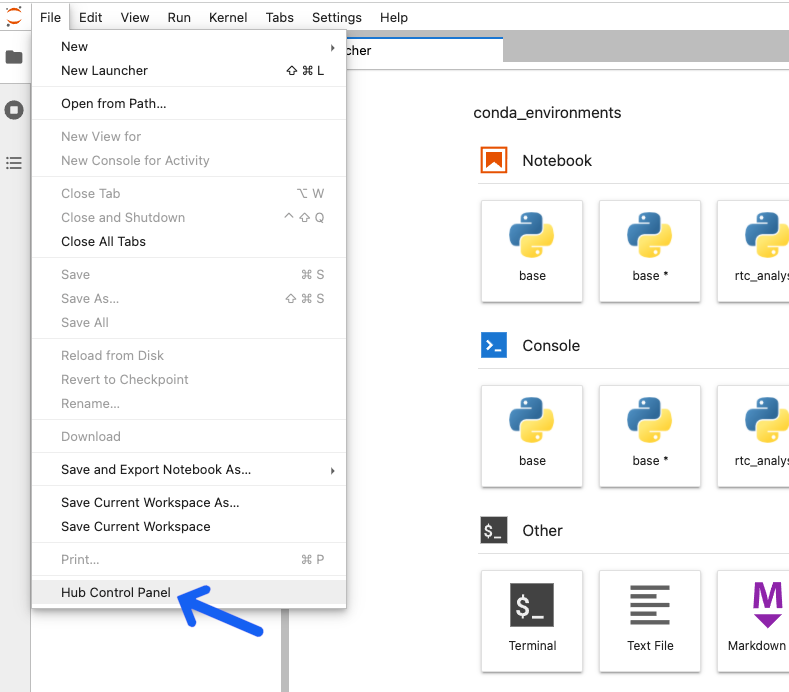
or
Click the
Shutdown and Logout Pagebutton in the upper right corner of the screen.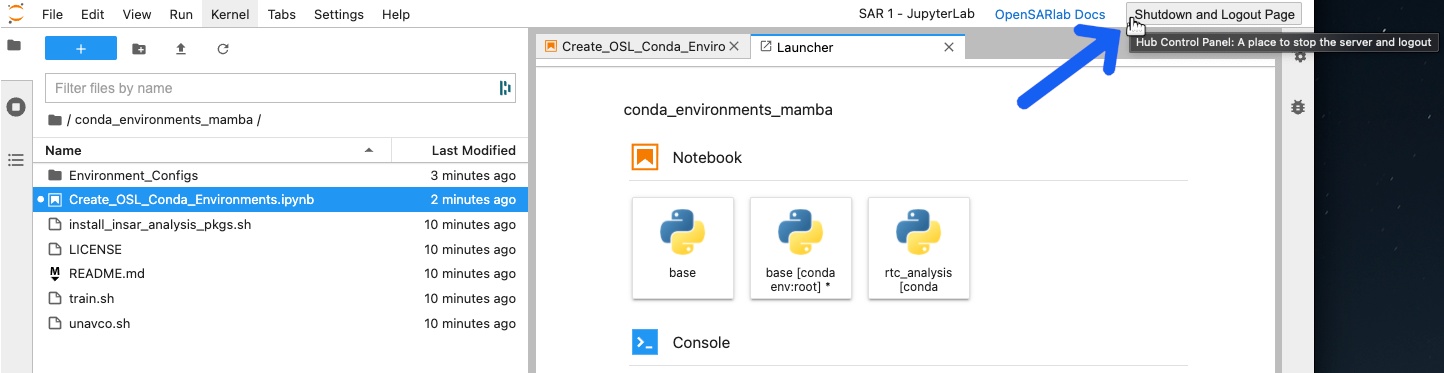
-
Click the
Stop My ServerButton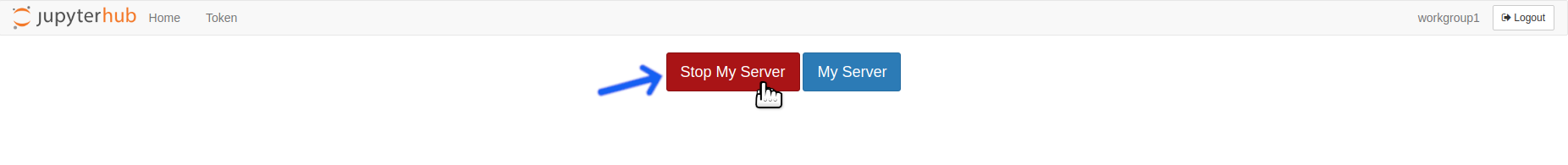
-
Click the
Start My ServerButton, which may take a few seconds to appear.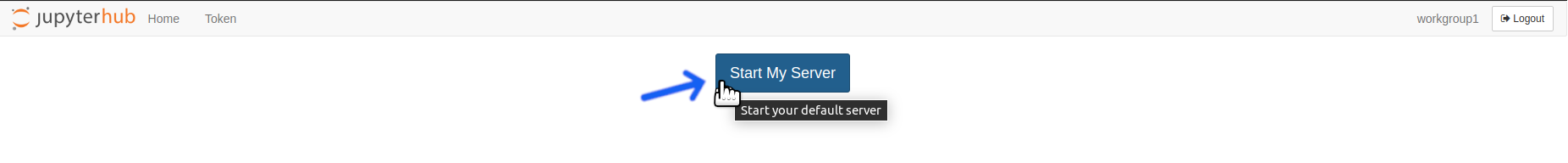
-
Click The
Launch ServerButton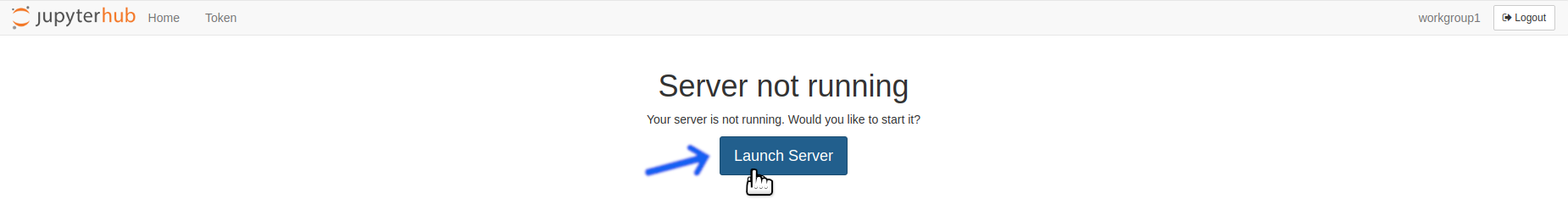
-
Select a Server Profile and Click the
Startbutton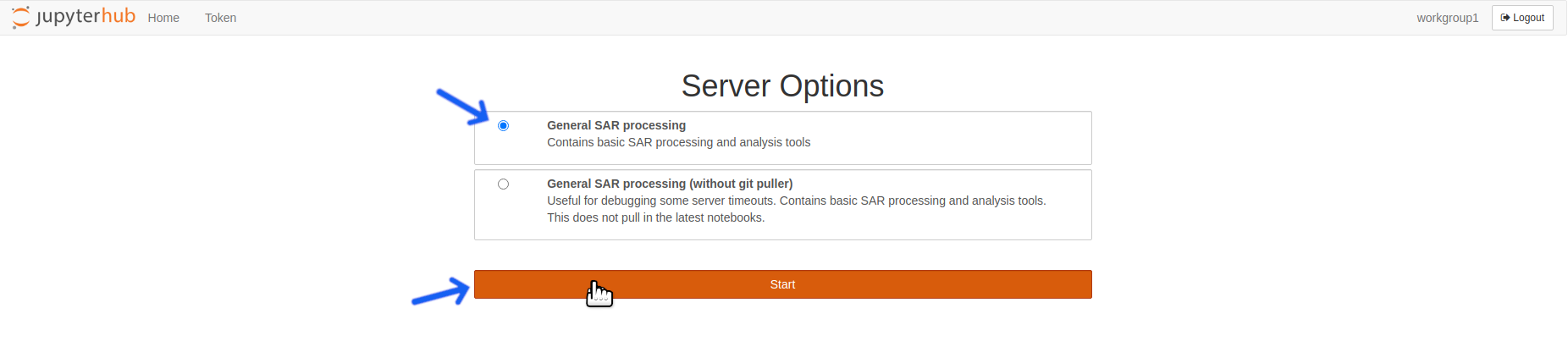
-
Wait for the server to start; this may take some time.
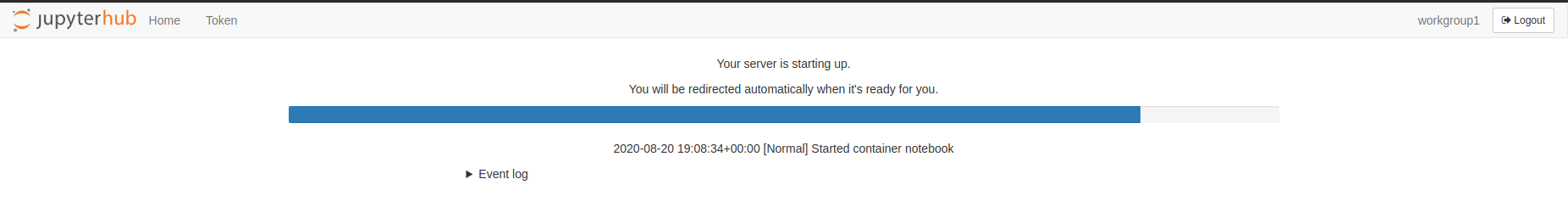
-
Optional: Click The
Event Logarrow for detailed startup status information. You may use this information to send a report to the admin if your server does not start.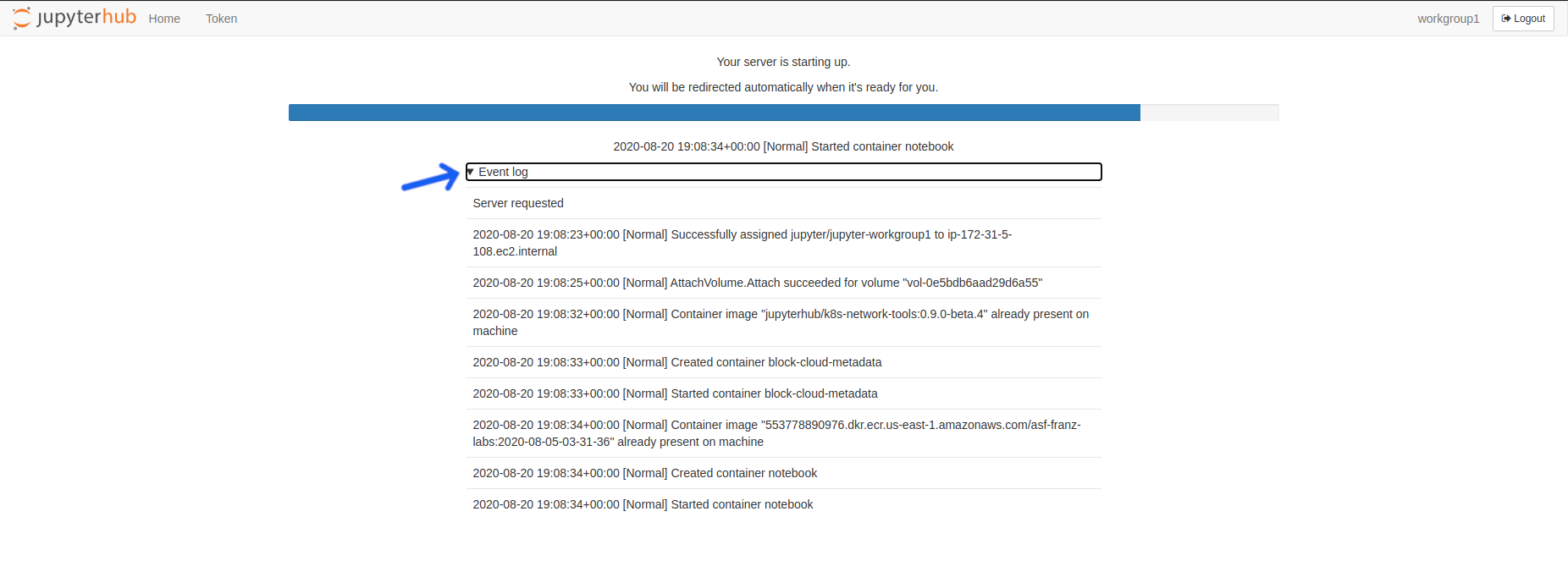
Changing a Notebook Kernel
Overview
Notebooks in OpenScienceLab run in a variety of conda environments. Since each kernel has different packages, you must pick the right one to confirm it has the required packages.
How to Switch Kernel
- Click the upper right corner. It should have the name of the
kernelthat you are currently using. -
A window with a list of built
kernelwill pop up. Select whicheverkernelyou need.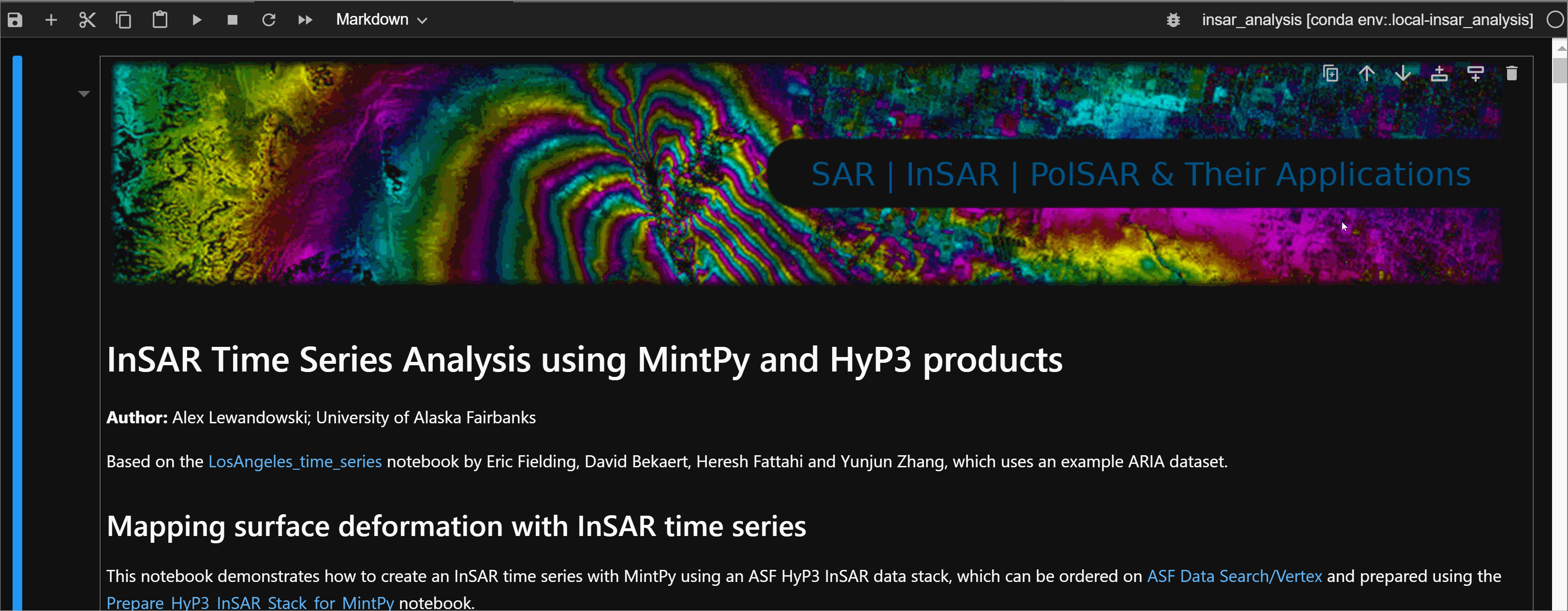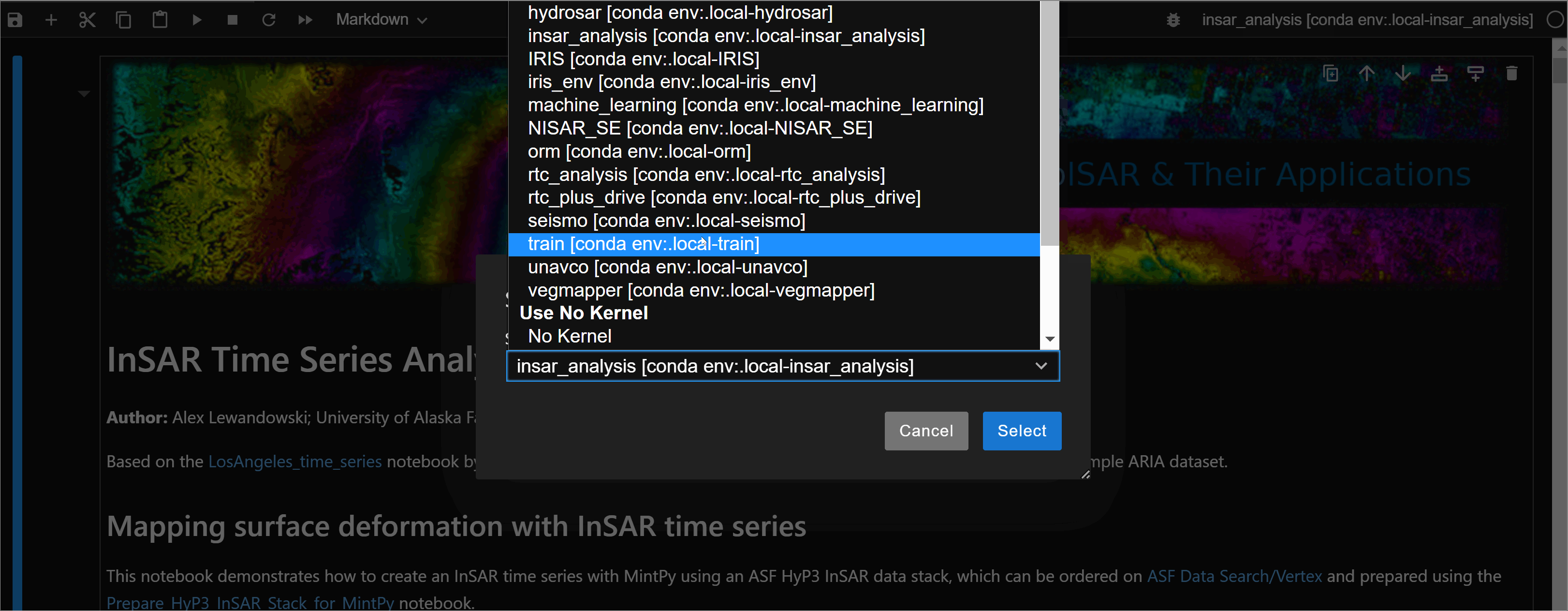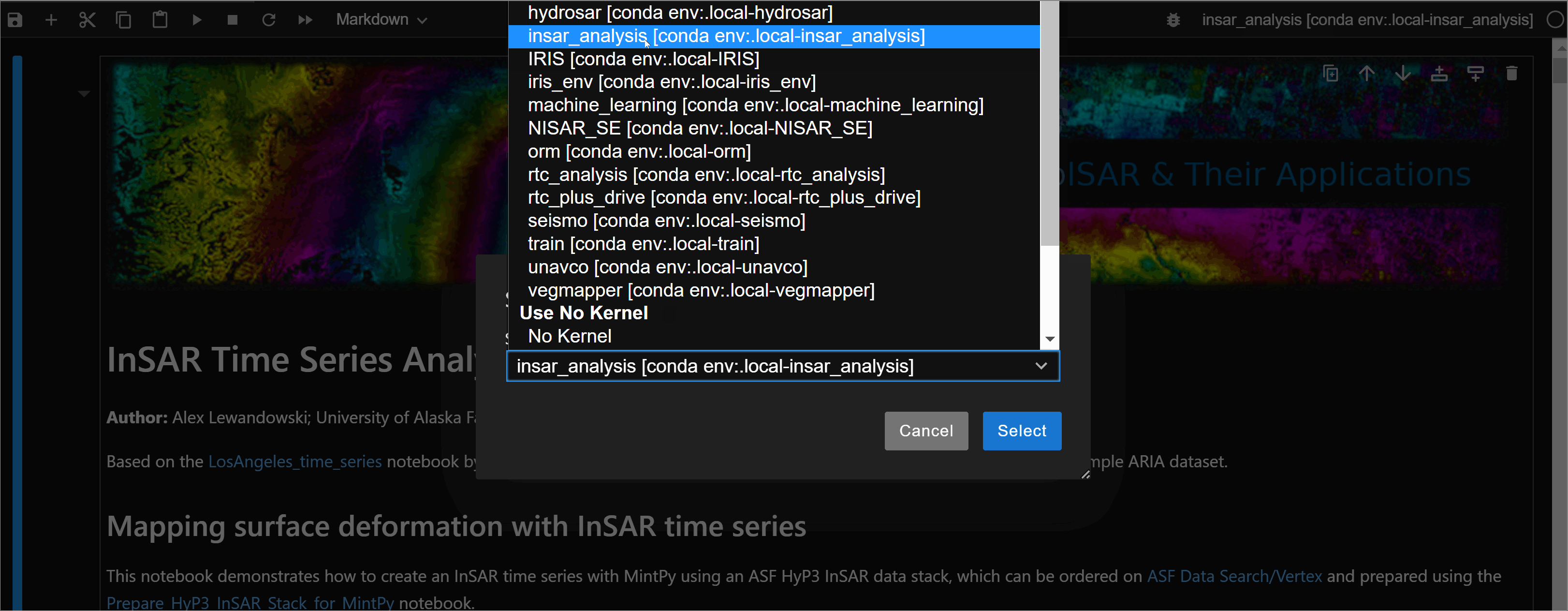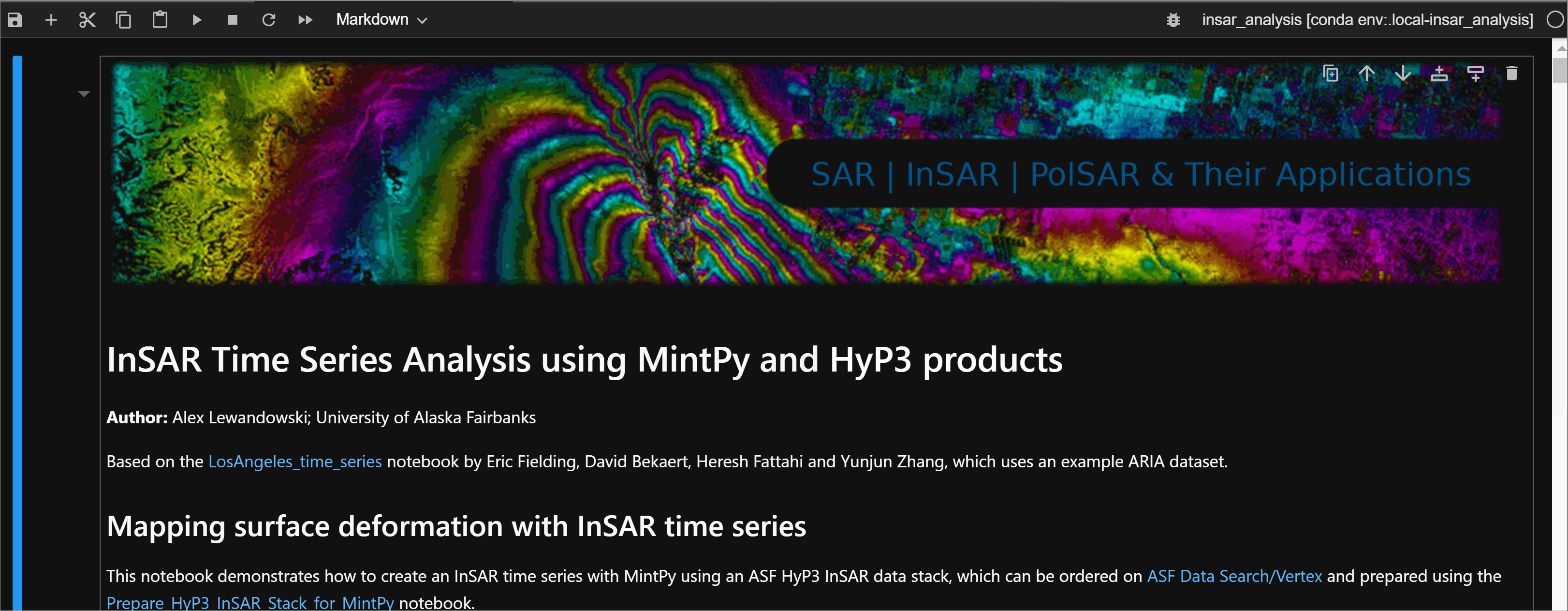
NB: To build a kernel, refer to the conda environments section.
Restarting a Jupyter Notebook Kernel
Overview
Variables and their assigned values are stored in memory as you run code cells in a notebook. As a result, rerunning a previously ran notebook without restarting the kernel may trigger some issues.
Uncleared variables are problematic for various reasons, such as:
- Increase the file size of the notebook.
- They occupy limited memory resources.
- *Previously defined values may cause unexpected results during the rerun ().
NB_: _Refer to the Rerunning a Notebook section in the How to Run a Jupyter Notebook* section.
The solution for this is to restart the kernel to clear notebook data.
How to Clear Notebook
Select one of the following from the Kernel Menu:
Restart Kernel: Restarts the kernel but leave the old code cell output in place.Restart Kernel and Clear All Outputs...: Restarts the kernel and removes old code cell output. This is generally the preferred option.Restart Kernel and Run up to Selected Cell...: Restarts the kernel and run up to the cell where you selected.-
Restart Kernel and Run All Cells...: Restarts the kernel and runs all the code cells. This only works if the notebook does not require input from the user.For most use cases, select
Restart Kernel and Clear All Outputs...